As the years go by, many of us shy away from soaking up the sun. We turn to hats and long cover-ups, worshipping broad spectrum sunscreen over bronzing. And rightfully so, knowing that sun exposure causes up to 80% of the visible signs of skin aging.
But the sun isn’t public enemy number one. Its health benefits keep us energized and its mood-boosting effects give us that finally-summer-feeling we know and love. So if you’re curious about how to enjoy the sun while protecting your skin, learning about different types of solar and ultraviolet (UV) radiation is key.
Table of Contents
What is the solar spectrum and how does it affect my skin?
The sun plays a vital role in our health, contributing to our mental well-being and playing a role in the synthesis of vitamin D. But it also emits something called electromagnetic radiation. While some of it is absorbed, scattered, and reflected before it reaches the Earth, the radiation that reaches us is called the solar spectrum.
The solar spectrum is made up of different kinds of radiation which are grouped by their electromagnetic frequencies. A few of them, like ultraviolet A radiation (UVA) and ultraviolet B radiation (UVB), should sound familiar. However, visible blue light and infrared radiation may also alter your skin’s appearance.
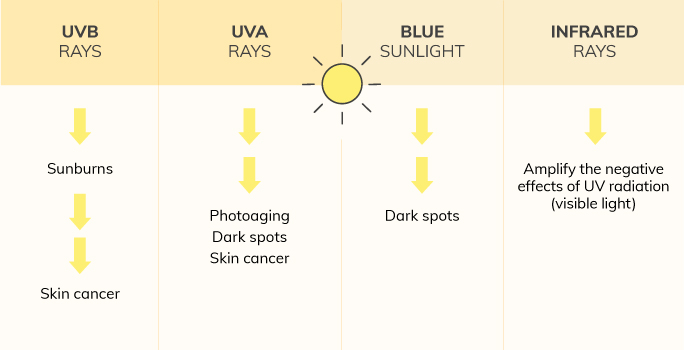
This solar radiation spectrum above ranges from the most powerful rays (ultraviolet) to the least powerful (infrared). Let’s find out how each affects your skin.
What’s the difference between UVA & UVB radiation?
UVB radiation
Responsible for summertime tan lines, these rays mainly affect the skin’s surface. Exposure to UVB radiation occurs outdoors and varies by time of day, location, and weather.
Although UVB radiation only reaches the outermost layer of your skin, it can also have lasting effects. Dr. Aurora Garre, ISDIN Medical Director, explains that UVB radiation is “the main cause of short-term skin damage” such as sunburns.
Fortunately, our bodies’ antioxidant systems can help repair DNA damage caused by overexposure to UVB radiation. But, repeated sunburns can dampen our natural regenerative capacity, increasing our risk of skin cancer.
UVB Radiation cheatsheet
Main skin concern: Sunburns and their role in skin cancer
Where does exposure happen? Outdoors in all weather conditions, although levels vary
Extra credit: When we talk about SPF we refer to the sun protection factor against UVB radiation. Protection ranges from minimal (SPF 2 to less than 12), moderate (SPF 12 to less than 30), and high (SPF 30 or higher).
UVA radiation
On the other hand, “UVA radiation is responsible for long-term damage, such as photoaging and skin cancer,” says Dr. Garre. It deeply penetrates the skin and breaks down collagen, contributing to the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles. UVA radiation can also produce photo immunosuppression and is the main cause of solar allergies.
Unlike UVB, UVA rays reach your skin even on cloudy days and inside your car, office, or house. So remember, it’s crucial to protect yourself with sunscreen daily, year-round.
UVA Radiation cheatsheet
Main skin concern: Signs of skin aging, sun allergies, and skin cancer
Where does exposure happen? Indoors and outdoors, year-round
Extra credit: Opt for sunscreen labeled as broad spectrum — meaning it meets FDA standards for UVA protection. And the higher the SPF, the higher the UVA protection will be too.

Can other types of solar radiation affect my skin?
Solar blue light
We can thank this type of sun-power for the gift of sight. Blue light is a high-energy visible light within the range of radiation the human eye can see. Reaching us both indoors and outdoors, we’re exposed to solar blue light every day.
But it’s not all good news. Recent studies have shown that solar blue light is linked to the appearance of dark spots or uneven pigmentation, especially in people with darker skin tones. And its synergistic effect with ultraviolet radiation has also been found to pose harm to the skin.
Solar blue light cheatsheet
Main skin concern: Dark spots and uneven pigmentation
Where does exposure happen? Indoors and outdoors, year-round
Extra credit: The damage that blue sunlight can cause has often been linked to artificial sources of blue light, such as cell phones or laptops. But, don’t cancel that stream session just yet. Solar blue light is 100 to 1000 times more intense than the blue light emitted by displays — making upping your sunscreen use the priority over cutting screen time.
Infrared radiation
Infrared radiation is different from UV radiation in a few ways. The most noticeable? It’s hotter. While we can’t feel UV radiation, our skin absorbs Infrared-A rays from the sun, causing that warm, sunny feeling. Used in physiotherapy treatments, this type of radiation can provide relief and reduce muscle pain with intense, localized heat.
But along with its healing properties come drawbacks as well. Even though infrared radiation is the least powerful type of solar radiation, it can still penetrate the skin and produce harmful oxidative stress. It also acts in tandem with ultraviolet radiation, further increasing the signs of photoaging.
Infrared radiation cheatsheet
Main skin concern: Amplifying the signs of skin aging
Where does exposure happen? Indoors and outdoors
Extra credit: Did you know that working in high-temperature environments can actually make you appear older? Extreme temperatures (via infrared radiation A) have been shown to increase the appearance of skin aging. And temperature is just one of the exposome factors that affect the way your skin looks.
Just the FAQs
Is there a relationship between UV radiation and skin color?
Anyone can experience the harmful effects of solar or UV radiation, no matter their skin color. And those effects can include skin cancer — making it incredibly important to use proper sun protection
But, some people are more likely than others to have their skin damaged by UV rays, like those who:
- Have lighter skin tones
- Had repeated sunburns during childhood
- Use or have used indoor tanning beds
- Have a history of skin cancer in the family
- Are 50 years of age or older
- Use certain medications or cosmetics that can make your skin and eyes more sensitive to UV radiation (including some types of antibiotics, birth control pills, and topical medicines)
How do melanocytes help protect the skin from UV radiation?
It’s true that melanin helps protects you from the sun’s ultraviolet rays. But how? In the outermost layer of your skin, you have pigment cells called melanocytes. These cells are in charge of melanogenesis: the way skin reacts to UV radiation (mainly UVA rays and blue sunlight) by producing melanin.
Melanin is a protective pigment and a form of natural coloring. So when you’re in the sun, your skin reacts by producing more melanin as a defense mechanism against sun exposure. And that’s why a sun tan or a sunburn is a sign of sun exposure.
How can I protect myself?
Knowledge is power! Solar radiation plays a positive role in our day-to-day lives, but uncontrolled exposure can pose health risks.
Understanding the effects of different types of solar and UV radiation can help you make smart decisions about daily sun protection. Discover our line of high SPF, broad spectrum sunscreens to help protect and repair your skin.
And above all, love your skin, care for it, and protect it, always.
References:
GW Lambert, C Reid, DM Kaye, GL Jennings, MD Esler, Effect of sunlight and season on serotonin turnover in the brain, The Lancet, Volume 360, Issue 9348, 2002, Pages 1840-1842 Jean Krutmann, Anne Bouloc, Gabrielle Sore, Bruno A. Bernard, Thierry Passeron, The skin aging exposome, Journal of Dermatological Science, Volume 85, Issue 3, 2017,Pages 152-161 Duteil L, Queille-Roussel C, Lacour JP, Montaudie H, Passeron T. Short-term exposure to blue light emitted by electronic devices does not worsen melasma. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2019. Khmaladze I, Leonardi M, Fabre S, Messaraa C, Mavon A. The Skin Interactome: A Holistic "Genome-Microbiome-Exposome" Approach to Understand and Modulate Skin Health and Aging. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2020;13:1021-1040. Published 2020 Dec 24. Cho, S., Shin, M., Kim, Y. S., Seo, J., Lee, Y. H., Park, C. H., & Chung, J. W. (2009). Effects of Infrared Radiation and Heat on Human Skin Aging in vivo. Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings, 14(1), 15–19. https://doi.org/10.1038/jidsymp.2009.7












